Avian Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV) - A Major Threat In Poultry Health
Avian Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV)
A Major Threat In Poultry Health
Avian Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD), caused by the Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV), remains one of the most economically impactful diseases in global poultry production. The virus primarily targets young chickens and causes severe immunosuppression, making affected flocks highly vulnerable to secondary infections and vaccination failures.
What Is IBDV?
IBDV is a highly contagious, resilient double-stranded RNA virus belonging to the Birnaviridae family.
Its hallmark feature is its tropism for the bursa of Fabricius, a key immune organ in young birds. Damage to this organ leads to:
- Reduced immune function
- Poor vaccine responses
- Increased mortality and production losses
Who Is Most at Risk?
The disease mainly affects:
Chickens aged 36 weeks, when the bursa is fully developed and highly susceptible.
Commercial broiler and layer operations, especially in areas with high poultry density.
Clinical Signs
In affected flocks, common clinical symptoms include:
- Sudden onset of depression
- Ruffled feathers
- Reduced feed intake
- Watery diarrhea
- Rapid drop in performance
- Increased mortality, often within 4872 hours
Subclinical infections may occur as well, causing no obvious symptoms but significant immunosuppression, leading to economic losses that are easily overlooked.
Why IBDV Remains a Global Challenge
Several factors contribute to the persistent worldwide burden of IBD:
- Highly stable in the environment, surviving months in houses and equipment
- Continuous emergence of variant and very virulent strains
- Vertical and horizontal transmission risks
- Difficulty maintaining adequate biosecurity in large poultry operations
Importance of Rapid Detection
Timely diagnosis is essential to:
- Confirm clinical outbreaks
- Differentiate IBD from other immunosuppressive diseases
- Guide farm-level control decisions
- Reduce further spread within and between farms
Modern rapid diagnostic tests support:
- On-farm detection
- Real-time disease monitoring
- Faster response and outbreak containment
Control and Prevention
Effective control measures include:
Strong biosecurity
Consistent vaccination strategies
Monitoring of vaccine strain effectiveness
Routine flock surveillance
When combined with rapid testing, these measures help poultry producers minimize losses and maintain flock health.
Summary
Infectious Bursal Disease continues to challenge poultry operations worldwide due to its:
- High contagiousness
- Environmental resilience
- Immune system damage
- Economic impact
Strengthening surveillance, adopting rapid diagnostics, and maintaining strong vaccination and biosecurity programs are key to staying ahead of this costly pathogen.
Source Of Information : https://www.vet-diagnostix.com/info/avian-infectious-bursal-disease-virus-ibdv-103222476.html
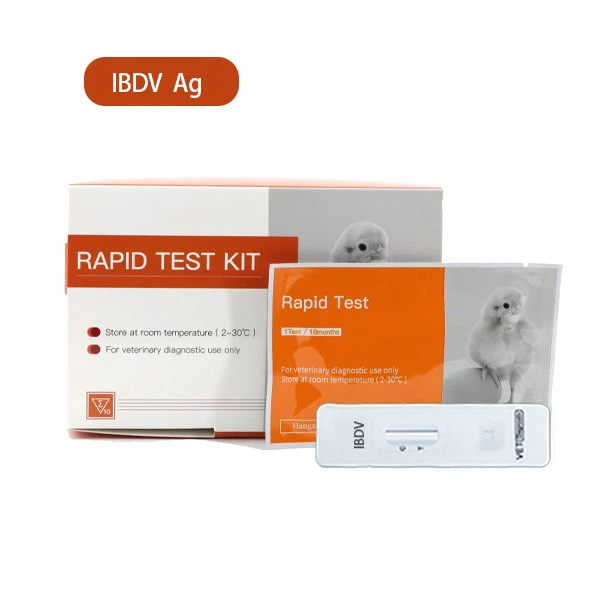
Recommended Test Kits